Associate Professor
We use computational modelling to probe various chemical processes which are important in the environment, catalysis and nanotechnology. We study small molecules, nano-structures, surfaces or bulk solids, employing electronic structure methods based on Density Functional Theory (DFT) and predict their structures, energies, optical properties etc. We also study electronic transport in molecules and nanostructures to look for systems which can perform molecular electronic functions, like sensing, switching or rectifying. At present, we are interested in theoretical modelling of materials which may have potential application in energy storage devices and exploration of new catalysts for energy conversion, as these problems are at the core of sustainable development.
Contact: bidisa.das@tcgcrest.org

PhD Scholars
Main Research Directions
Natural nano-structures and minerals for catalysis
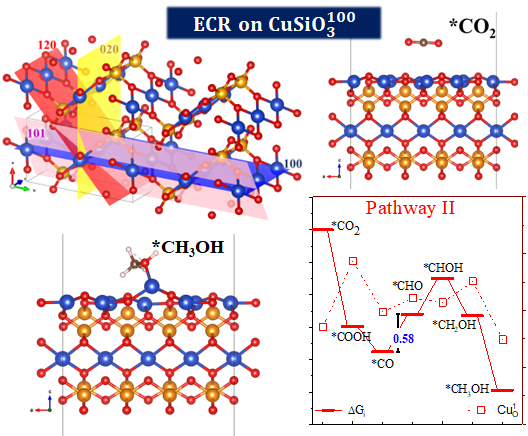
Reduction of CO2 to ethanol on CuSiO3, a silicate mineral
Applied Physics Reviews, 13, 011410 (2026). doi.org/10.1063/5.0284285
The electronic structure of orthorhombic CuSiO3, derived from mineral dioptase, is investigated for electrocatalytic carbon di oxide reduction (ECR) reactions. Compared to the traditionally employed Cu [111] and CuO [111] surfaces, the CuSiO3 [100] surface allows for superior CO2 adsorption due to its ideal positioning of the d-band centre closer to the Fermi energy, accessible conduction band states, multivalent surface Cu atoms and negligible HER. Our studies show that a lower barrier height (0.58 eV) for the formaldehyde pathway through CO formation, not only governs the feasibility of the reaction but also ensures product selectivity for methanol formation through an efficient ECR. An analysis of the free energies of the intermediates and magnetic moments of the active Cu sites shows a direct correlation between the barrier height and change in the magnetic moment .
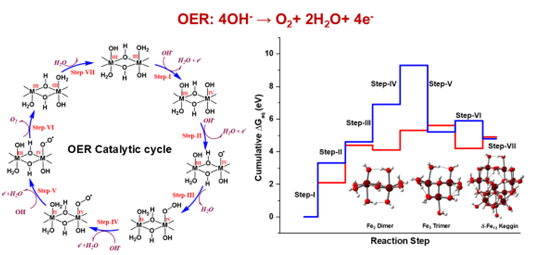
A DFT Investigation on Pure & Doped Fe-Oxyhydroxide Clusters for homogeneous, electrocatalytic Oxygen Evolution Reaction
ACS Applied Energy Materials. 9, 629 (2026). doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.5c03431
In this study, we investigate the electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction (OER) using Fe-oxyhydroxide nanoclusters in a homogeneous aqueous medium, employing density functional theory (DFT) investigations. A water molecule coordinated to the Fe center of the Fe(III) oxyhydroxide cluster was converted to oxygen, in few sequential stepwise electron transfer reactions analogous to conventional OER. We first studied the free energy changes of OER using small Fe(III) oxyhydroxide clusters and evaluated the effects of doping with Co, Ni, and Mn on their OER activity. The OER activities of larger delta-Fe13 Keggin clusters showed reduced OER activities compared to the Fe2 dimers, Fe3 trimers, however, Co(III) doping enhanced the OER activity showing an overpotential of ~1.07 V. The better performance of the Co(III) doped Fe(III) oxyhydroxide clusters were then rationalized in terms of the stabilities of oxyl radical species centered on Co(III) center compared to Fe(III) center of the oxyhydroxide clusters.
Research project started in February 2024, titled “ Designing efficient electrocatalysts from studies of natural minerals in multidimensional hybrid systems using density functional theory“, funded by DST-SERB.
Dimerization of Fe(III) Ion in an Aqueous Medium: Mechanistic Modelling and Effects of Ligands
ChemPhysChem, 25,e202400144 (2024). doi.org/10.1002/cphc.202400144
Abstract: Aqueous iron solutions generally undergo spontaneous hydrolysis followed by aggregation resulting in the precipitation of nanocrystalline oxyhydroxide minerals. The mechanism of nucleation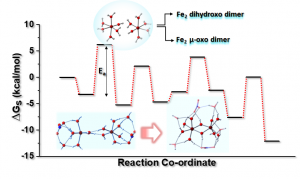 of such multinuclear oxyhydroxide clusters are unclear due to limited experimental evidence. Here, we investigate the mechanistic pathway of dimerization of Fe(III) ions using density functional theory (DFT) in aqueous medium considering effects of other ligands. Two hydrolyzed monomeric Fe(III) ions in aqueous medium may react to form two closely related binuclear products, the m-oxo and the dihydroxo Fe2 dimer. Our studies indicate that the water molecules in the second coordination sphere and those co-ordinated to the Fe(III) ion, both participate in the dimerization process. The proposed mechanism effectively explains the formation of dihydroxo and μ-oxo Fe2 dimers with interconversion possibilities, for the first time. Results show, with only water molecules present in the second co-ordination sphere, dihydroxo Fe2 dimer is the thermodynamically and kinetically favored product with a low activation free energy. We calculated the step-wise reaction free energies of dimerization in the presence of nitrate ions in the first and second coordination sphere of Fe(III) ion separately, which shows that with nitrate ions in the second co-ordination sphere, the μ-oxo Fe2 dimer is the kinetically favored product.
of such multinuclear oxyhydroxide clusters are unclear due to limited experimental evidence. Here, we investigate the mechanistic pathway of dimerization of Fe(III) ions using density functional theory (DFT) in aqueous medium considering effects of other ligands. Two hydrolyzed monomeric Fe(III) ions in aqueous medium may react to form two closely related binuclear products, the m-oxo and the dihydroxo Fe2 dimer. Our studies indicate that the water molecules in the second coordination sphere and those co-ordinated to the Fe(III) ion, both participate in the dimerization process. The proposed mechanism effectively explains the formation of dihydroxo and μ-oxo Fe2 dimers with interconversion possibilities, for the first time. Results show, with only water molecules present in the second co-ordination sphere, dihydroxo Fe2 dimer is the thermodynamically and kinetically favored product with a low activation free energy. We calculated the step-wise reaction free energies of dimerization in the presence of nitrate ions in the first and second coordination sphere of Fe(III) ion separately, which shows that with nitrate ions in the second co-ordination sphere, the μ-oxo Fe2 dimer is the kinetically favored product.
Molecular adsorption on surfaces
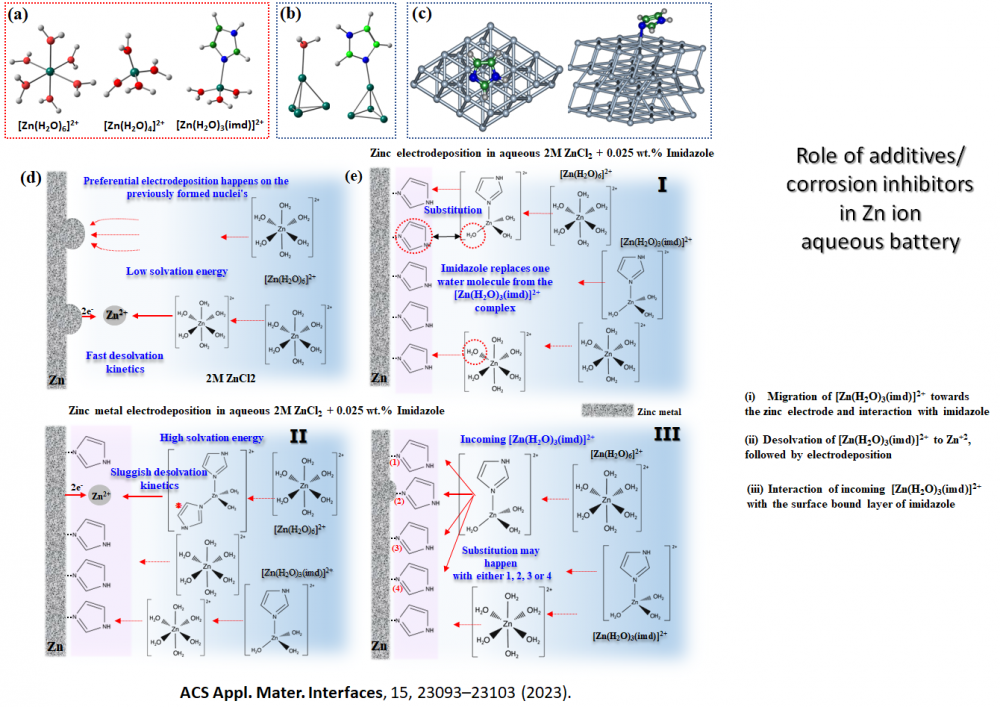
Designing additives and modelling corrosion inhibition (Zn ion battery)
Amide Additives Enhance the Understanding of Kinetic Reversibility in Zinc Anode Stability Using Ultramicroelectrodes, J. Nguyen , A. Rana , K. Shiprath , B.R. Bhagat , S. Paul , S. Chatterjee , N. Roy , I. Das, Bidisa Das*, A. Banerjee* and J. E. Dick*, Chemical Science, (2025) DOI:10.1039/D5SC06311F .
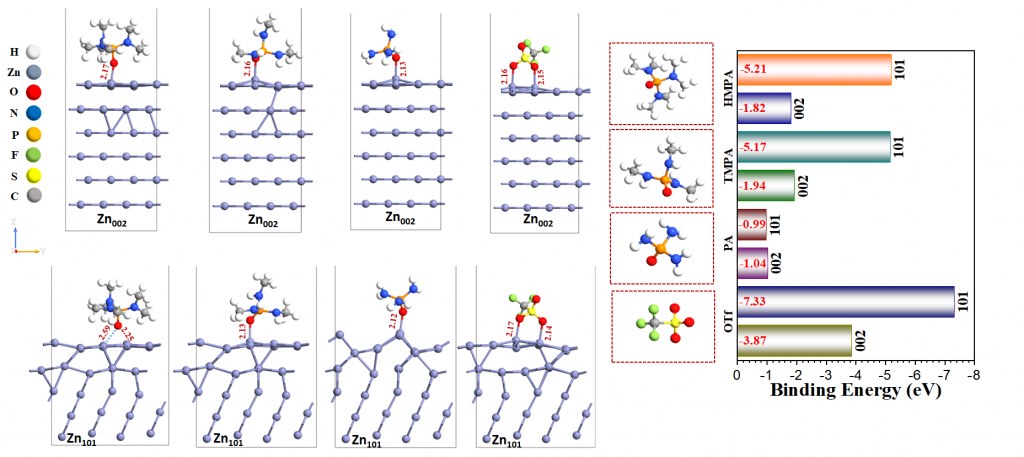
Modulation of Electron Push-Pull by Redox Non-Innocent Additives for Long Cycle Life Zinc Anode A. Manna, Bidisa Das,* S. Ogale, and M. K. Bhunia*, SMALL (2024). doi.org/10.1002/smll.202404752
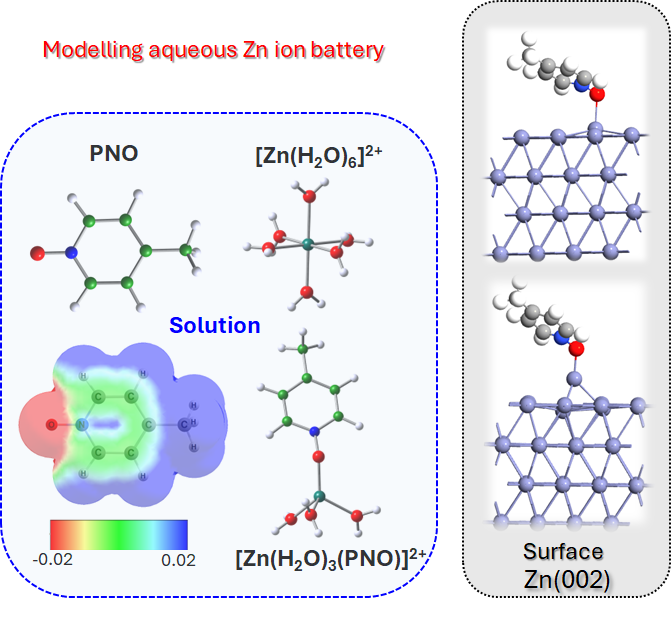
Mitigating Dendrite Formation on a Zn Electrode in Aqueous Zinc Chloride by the Competitive Surface Chemistry of an Imidazole Additive. A. Rana, A. Thakare, N. Kumar, B. Mukherjee, A. Torris, Bidisa Das, S. Ogale, A. Banerjee, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 15, 23093–23103 (2023).
Lithiophilicity of (B,N) doped graphene surface
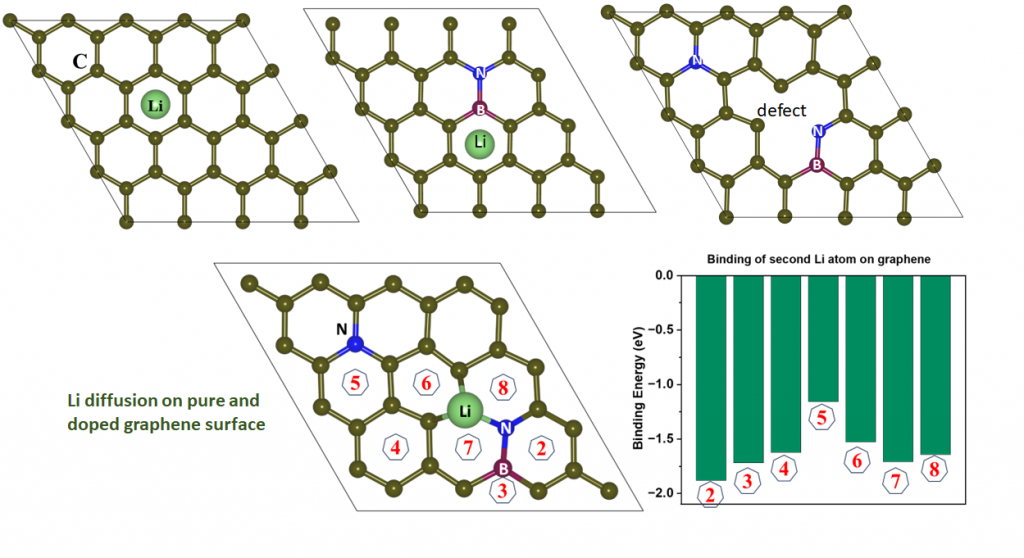
Light element (B, N) co-doped graphitic films on copper as highly robust current collectors for Anode-Free Li metal battery applications, R. Godbole, S. Hiwase, M. Hossain, M. Wable, S. Rane, S. Mandal, Bidisa Das*, A. Banerjee*, S. Ogale*, Applied Physics Reviews (2024). (In press)
Metal complexes encapsulated in zeolite pores for catalysis
Modelling of nano-electronic devices
Modelling of electronic structure and electronic transport properties of functional molecules, nanoclusters, quantum dots and nano ribbons in two-probe junctions using DFT and NEGF formalism.
Academic Profile
- Scientist D, 2019-2022, Technical Research Center (TRC), IACS. Jadavpur, Kolkata.
- Research Associate III, 2015-2019, IACS, Jadavpur, Kolkata.
- Scientist (DST Fast Track), 2012-2015, IACS, Jadavpur, Kolkata.
- Research Associate III, 2010-2012, IACS, Jadavpur, Kolkata.
- Scientist (DST WOS-A), 2007-2010, IACS, Jadavpur, Kolkata.
- Post Doctoral Researcher, 2004-2006, Nanotechnology Research Institute, AIST, Tsukuba, Japan.
Education
- PhD, 2004, Theoretical Chemistry, Thesis Supervisor: Professor K. L. Sebastian, Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bangalore, India.
- MSc, 1997, Chemistry (Physical Chemistry), University of Calcutta.
- BSc,1995, Chemistry (Hons.),University of Calcutta.
Publications
Recent Journal Publications
- Role of Cu^d+ sites for a favorable electrocatalytic CO_2 reduction on CuSiO_3 surface. Brajesh Rajesh Bhagat, Bidisa Das, Applied Physics Reviews, 13, 011410 (2026). doi.org/10.1063/5.0284285
- Dual-Functional Medium-Entropy Quinary Sulfides for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution and Ethylene Glycol Oxidation. T. Bagaria, B. R. Bhagat, S. Ghosh, A. Ambalkar, Bidisa Das, B. Debnath, Langmuir, 42, (2026). doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5c05570
- DFT Investigation on Pure and Doped Fe-Oxyhydroxide Clusters for Homogeneous, Electrocatalytic Oxygen Evolution Reaction. S. De, Bidisa Das, ACS Applied Energy Materials. 9, 629 (2026). doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.5c03431
- Amide Additives Enhance the Understanding of Kinetic Reversibility in Zinc Anode Stability Using Ultramicroelectrodes, J. Nguyen , A. Rana , K. Shiprath , B.R. Bhagat , S. Paul , S. Chatterjee , N. Roy , I. Das, B. Das, A. Banerjee and J. E. Dick, Chemical Science, (2025) DOI: 10.1039/D5SC06311F .
- Efficient oxidative coupling of amines to imines under natural sunlight using a benzothiadiazole-based molecular photocatalyst, Ajeet Singh, Bidisa Das, Saumi Ray, Materials Advances, 6, 1667-1678 (2025). DOI https://doi.org/10.1039/D4MA00990H
- Key Anodic Interfacial Phenomena and their Control in Next‐Generation Lithium and Sodium Metal Batteries,Kingshuk Roy, Manas K. Bhunia, Pitchiah E. Karthik, Ashutosh Rana, Bidisa Das, Abhik Banerjee, Satishchandra Ogale, Small, 21, 2410167(2025). doi.org/10.1002/smll.202410167
- Earth-Abundant 3d-Transition Metal Metasilicates as Effective Electrocatalysts for Alkaline HER: CuZnSiO3 Outperforms CuSiO3 and ZnSiO3, Trupti Ghogare, Indrajit Patil, Mujaffar Hossain, Richa Bobade, Sukanata Mondal, Su Varma, Bidisa Das, Satishchandra Ogale, ChemSusChem, 18, e202402043(2025). doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202402043
-
Molecular Propeller Tethering on a Dipeptide Induces a One-Step Conversion of Its Secondary Structure on Water Surface Promoted by Chiral Supramolecular Assembly, Sandip Biswas, Umesh, Bidisa Das, Pradyot Koley, Somobrata Acharya, Santanu Bhattacharya Small,21, 2408634 (2024).doi.org/10.1002/smll.202408634
- Light element (B, N) co-doped graphitic films on copper as highly robust current collectors for Anode-Free Li metal battery applications, Rhushikesh Godbole,Shweta Hiwase,Mujaffar Hossain,Minal Wable,Sunit Rane,Sukanta Mandal, Bidisa Das, Abhik Banerjee, Satishchandra Ogale, Applied Physics Reviews 11, 031416 (2024). doi.org/10.1063/5.0208785
- Modulation of Electron Push–Pull by Redox Non-Innocent Additives for Long Cycle Life Zinc Anode, Arghyadip Manna, Souvik Pal, Bidisa Das, Satishchandra Ogale, Manas K. Bhunia, SMALL (2024). doi.org/10.1002/smll.202404752
- Dimerization of Fe(III) Ion in an Aqueous Medium: Mechanistic Modelling and Effects of Ligands, Sharmistha De, Bidisa Das, ChemPhysChem, 25,e202400144 (2024).doi.org/10.1002/cphc.202400144
-
Push–Pull Engine─Electron Pumping by Anchored Ligands over ZnO/C: Boosting Photo-Fenton-Like Catalysis without Additional Oxidants. Kajal Sharma, Ravinder Kaushik, Sharmistha De, Singh Astha, Rituporn Gogoi, Bidisa Das, Aditi Halder, Prem Felix Siril, ACS EST Engg. (2024). doi.org/10.1021/acsestengg.3c00626
- Sanjit Das, Sharmistha De, Paolo Centomo, Vinod K. Aswal, Carlo Meneghini, Bidisa Das, Sugata Ray, Structural Rearrangement Followed by Entrapment of Subnanometer Building Blocks of Iron Oxyhydroxide in Aqueous Iron Chloride Solutions, Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 16, 7255–7265. doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.4c00031
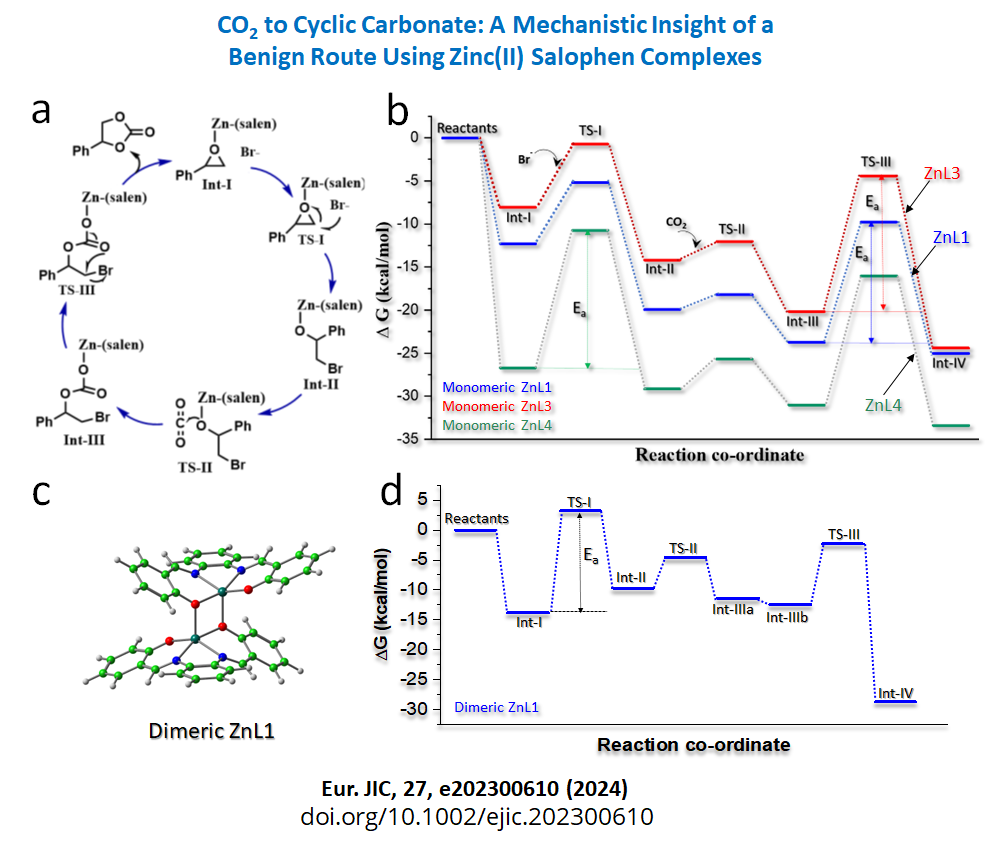
- CO2 to Cyclic Carbonate: A Mechanistic Insight of a Benign Route Using Zinc(II) Salophen Complexes, A. Ramesh, S. De, S. Bajaj, Bidisa Das, S. Ray,European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry,27, e202300610 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.202300610
-
Curious Behavior of Fe3+-As3+ Chemical Interactions and Nucleation of Clusters in Aqueous Medium. S. Das, G. Mishra, D. Halder, I. Carlomagno, C. Meneghini, G. De Giudici, Bidisa Das, A. Paul, V. K. Aswal, S. Ray, Inorg. Chem., 62, 30, 11966–11975 (2023).https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c01387
- Hierarchical Polyoxometallate Confined in Woven Thin Films for Single-Cluster Catalysis: Simplified Electrodes for Far-Fetched O 2 Evolution from Seawater, Kirti, P. Dobaria, A. Maurya, A. Kaushik, P. Kanani, P.Rajput, S. N. Jha, Bidisa Das, D. N. Srivastava, S. Kushwaha, K. Patel, ACS Catalysis, 13 , 4587-4596 (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.3c00544
- Mitigating Dendrite Formation on a Zn Electrode in Aqueous Zinc Chloride by the Competitive Surface Chemistry of an Imidazole Additive. A. Rana, A. Thakare, N. Kumar, B. Mukherjee, A. Torris, Bidisa Das, S. Ogale, A. Banerjee, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 15, 23093–23103 (2023). https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.3c01310
- Unlocking the electronic, optical and transport properties of semiconductor coupled quantum dots using first-principles methods. A. Chakraborty, Bidisa Das, I Dasgupta, J. Quantum Chem, 123, e27101(2023). https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/qua.27101
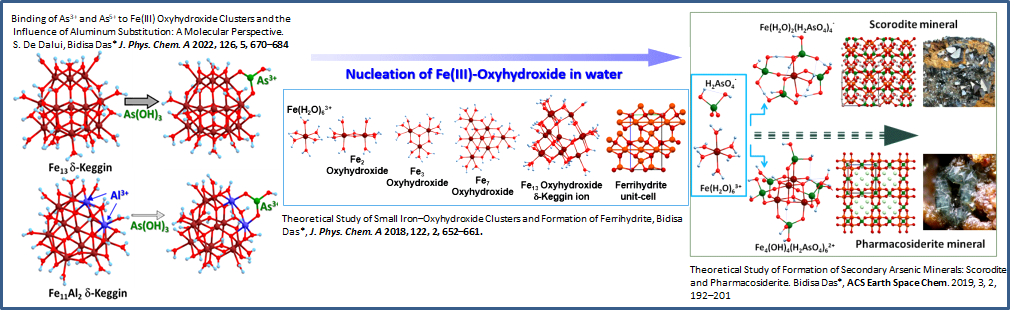
- Binding of As3+ and As5+ to Fe(III) Oxyhydroxide Clusters and the Influence of Aluminum Substitution: A Molecular Perspective, S. De Dalui, Bidisa Das J. Phys. Chem. A, 126, 670–684 (2022). http://DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.1c08754
- Origin of Intense Luminescence from Supramolecular 2D Molecular Crystals. S. Biswas, G. Manna, Bidisa Das, A. Bhattacharya, A. K. Pal, A. Datta, P. Alam, I. R. Laskar, P. Mondal, M. K. Mukhopadhyay, M. K. Sanyal, S. Acharya, Small, 2103212(1-9) (2021). DOI: 10.1002/smll.202103212
- Supramolecular Design Strategies for Color Tuning of Iridium(III) Complexes Using a Common Framework of Cyclometalating Ligands. S. Biswas, Bidisa Das, P. Alam, A. Ghatak, U. K. Ghorai, A. Ghosh, B. B. Das, I. R. Laskar, S. Acharya. J. Phys. Chem. C, 125, 4730-4742 (2021). DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c11570
- Zeolite-Y Encapsulated Cobalt(II) Schiff-Base Complexes Employed for Photocatalytic Dye-Degradation & Upcycling CO2 . S. Kumari, A. Ramesh, Bidisa Das, S. Ray. Inorg. Chem. Front., 8, 1553-1566 (2021). DOI: 10.1039/D0QI01190H
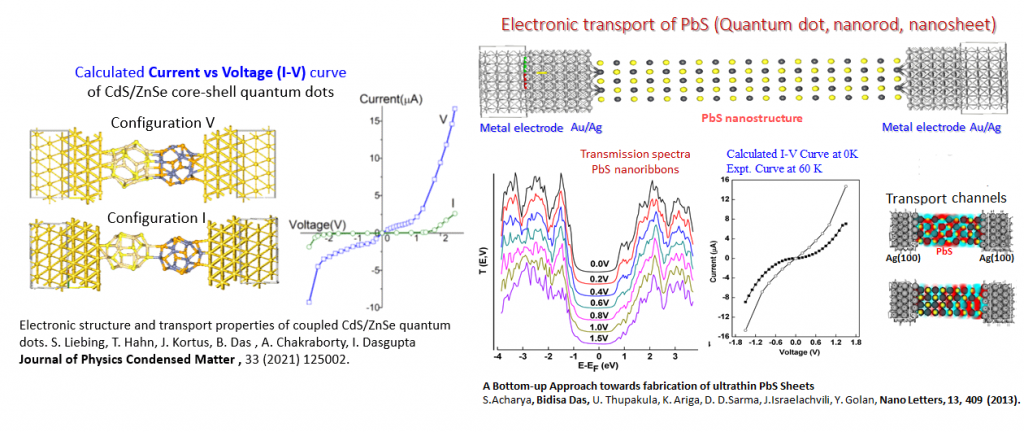
- Electronic structure and transport properties of coupled CdS/ZnSe quantum dots. S. Liebing, T. Hahn, J. Kortus, Bidisa Das, A. Chakraborty, I. Dasgupta, J. of Phys.: Cond. Matt., 33,125002 (2021). DOI: 10.1088/1361-648X/abd5f6
- Coagulating and flocculating ferrihydrite: application of zinc acetate salt. S. Islam, S. Das, G. Mishra, Bidisa Das, A. Malakar, I. Carlomagno, C. Meneghini, G. De Giudici, L. P. L. Goncalves, J. P. S. Sousa, Yury V. Kolen’ko, A Cristian Kuncser, S. Ray. Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 6, 2057-2064 (2020).DOI: 10.1039/D0EW00357C
- Molecular Distribution of Indomethacin: Impact on the Precipitation of Glassy Curcumin pH-Responsive Nanoparticles with Enhanced Solubility. K. Sharma, Bidisa Das, P. F. Siril, Crystal Growth & Design, 20, 2377-2389 (2020). DOI: 10.1039/D0EW00357C
- An insight into the catalytic activity of palladium Schiff-base complexes towards the Heck coupling reaction: routes via encapsulation in zeolite-Y. S. Kumari, Bidisa Das, S. Ray, Dalton Transactions, 48, 15942 (2019).
- Theoretical Study of Formation of Secondary Arsenic Minerals: Scorodite and Pharmacosiderite. Bidisa Das, ACS Earth and Space Chemistry 2, 192, (2019). https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.8b00124
- Theoretical study of small Iron-oxyhydroxide clusters and formation of Ferrihydrite. Bidisa Das, J. Phys. Chem. A, 122, 652 (2018).DOI:10.1021/acs.jpca.7b09470
https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=r5KXTTsAAAAJ&hl=en